Parasites are constantly present in the human body.These can be both pathogenic worms and amoebas, and protozoa that do not cause diseases and sometimes help to cope with the bacterial flora.Parasites that feed on the host, damage internal organs and disrupt the function of vital systems pose a health threat.
Classification of human parasites
There are different types of human parasites.Protozoa, arthropods and helminths live mainly inside the body and on its surface.Some organisms are constant companions of humans, others use them as a temporary reservoir for the transition to the next stage of development.
True parasites cannot live without a host and die in a free environment.False ones can feel the same in the human body, on the ground, in water and on surrounding objects.There are also hyperparasites that nest in similar creatures and live on them.Depending on the location, parasites are divided into:
- Internal.These are endoparasites that feed on intestinal juices, organ tissue, blood and lymph.
- External.They are called ectoparasites and live on the body, in the hair and in the folds of the skin.
- Material.Their habitat is the internal organs (liver, heart, lungs, gallbladder, brain).
- Cavity.These parasites live, feed and reproduce in the intestines and stomach.
- Intracellular or blood.They are usually microscopic and are found in biological fluids.
Note!
In addition to the general classification, there is an individual classification of all parasite species into species and classes.Protozoa can be represented by ciliates, sarcodes and amoebas.Worms are divided into flukes, tapeworms and roundworms.Arthropods include insects, arachnids and bloodsuckers.
What parasites do humans have?
Humans are equally commonly infected with protozoa and helminths.Insects are mainly diagnosed in socially disadvantaged people.Unlike children, adults can be infected with all known parasites.This is due to the diversity of dietary habits and the opportunity to travel.Many are misled by the misleading belief that parasitic diseases are primarily diagnosed in childhood.In fact, they are detected more often at an early age, but adults are no less likely to become ill than children;Their clinical signs of invasion can be easily erased.
Protozoa and their localization
These single-celled parasites live in the bodies of adults for decades;They are studied by the science of protozoology.They can cause both specific infections and general illnesses.Active individuals are called trophozoites and usually have flagella for locomotion.To continue the life cycle, protozoa have the ability to enclose themselves in capsules (cysts).These forms are immobile and persist for a long time in the external environment and in unfavorable conditions.
Many flagellate species parasitize adults.They have microscopic sizes and different localizations:
- Trichomonas affects the genitourinary system, oral cavity and prostate in men;
- Intestinal balantidia live in the lumen of the colon;
- Giardia parasitizes the liver, bile ducts and intestines;
- Malaria plasmodia destroy blood cells;
- Toxoplasma spreads through the bloodstream to all organs, including the brain;
- Trypanosomes attack the brain and cause “sleeping sickness”;
- Leishmania colonize in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver and bone marrow;
- Dysenteric amoebas live in the large intestine.

All protozoan species of parasites have a similar life cycle, which occurs through the transition from the vegetative stage to the cyst stage.Reproduction in unicellular organisms occurs both sexually and asexually.
Note!
Protozoa are true parasites and cannot exist in the trophozoite stage without a permanent or intermediate host.
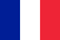
Diseases caused by parasites of the worm class
The presence of roundworms and flatworms is often detected in the body of adults.They differ in size, functional characteristics and the degree of negative impact on organs and systems.
Nematodes
There can be different types of these parasites in humans.They belong to the class of roundworms and resemble a spindle in appearance.Worms feel free in the host's body and in an open environment.The most common nematode pathogens include:
- Ascaris.Lives in the small intestine, is 20 to 40 cm long and reproduces sexually.
- Pinworm.A small worm, no longer than 12 mm.It attacks the intestines and can lay up to 15,000 eggs per day.The male dies after mating, the female after laying the larvae.
- Hookworm.Lives in the jejunum and duodenum.This parasite inside a human can suck up to 0.3 ml of blood per day, using sharp teeth to damage the intestinal wall.
- Whipworm.The worm, up to 5 cm long, lives in the intestine and, thanks to its unique body structure, sucks juices from the thickness of its walls.
- Trichinae.This is an intramuscular parasite measuring up to 4 mm in size that causes the dangerous disease trichinosis in humans.Trichinella looks like a spiral and is a viviparous helminth.
- Guinea worm.This parasite in the human body reaches 1 meter in length and looks like a thin white thread.The localization of Guinea worm can occur in the subcutaneous layer of the legs, back or lower abdomen.
- Filaria.They enter the body through the bites of infected mosquitoes, midges and horseflies.The habitat of the filariae is the entire circulatory and lymphatic system.They clog the blood vessels of the heart, lungs and other organs, causing obstruction.
- Toxocara.The worm's larvae travel through the body and infect the heart, lungs, liver and brain.The size of adult helminths reaches 18 cm.
- Intestinal eel.The pathogen that causes strongyloidiasis lives in the intestine when it is ripe.Eel larvae can spread throughout the human body via the bloodstream.
Important!
The negative effects of roundworms on the body are due to their mechanical and toxic effects.
Trematodes
These are parasites that live in humans and have the second name fluke.There are different species of these flatworms.They cause different diseases, but are similar in structure.All flukes have a leaf-shaped body with two suckers.Trematodes do not have an anus;digested food is excreted through the mouth.
Depending on the location, trematode parasites attack the body.Liver, lanceolate and catworms attack the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts.The lung fluke lives in the lungs, the leech lives in the blood vessels.
Note!
Flukes always have an intermediate host in the form of a variety of molluscs.
Cestodes
This species includes helminths from the class of tapeworms or tapeworms.They have a special structure and look like a chain of their individual fragments (strobilus).Cestodes parasitize in the intestines and release large amounts of toxins into the body.

Worms in this class commonly found in adults include:
- Wide tape.The largest parasite, up to 15 meters long, absorbs nutrients throughout the body and poisons the body with its toxins.
- Pork tapeworm.It is the causative agent of taeniasis, reaches 3 meters in length and is “armed” with several hooks.
- The bull tapeworm consists of more than a thousand segments and grows up to 10 meters long.
- Dwarf tapeworm.The size of the worm is no more than 5 cm;It lives in the human body for about two months and then dies.
- Echinococci and alveococci.Helminths cause liver and lung disease and can form larval blisters in internal organs.
Note!
Cestodes are particularly dangerous due to their ability to parasitize in the form of cysticerci.These are encapsulated larvae that enter all organs via the bloodstream and cause mass invasion.
External parasites
The most common ectoparasite living in the human body is the louse.It lives in the scalp, armpits, groin, beard and even eyelashes and eyebrows.The disease caused by parasites is called pediculosis.Depending on the location, a distinction is made between body, pubic and head lice.You can get rid of insects using external means in the form of shampoos, ointments and solutions.
Important!
The danger of lice is that they can transmit typhus, a serious infectious disease, through saliva.
Symptoms of parasites in the human body
With external insects such as lice and fleas everything is clear;They manifest themselves through local itching and the formation of wounds at the bite sites.Internal parasites cause a more diverse clinical picture.This depends on the location of foreign organisms, their size and the extent of the invasion.

Hundreds of worms and protozoa of the same or different species can parasitize humans at the same time.Parasites can live unnoticed in humans for several years and do not cause any specific symptoms.The most common signs of an infestation usually include:
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- Weakness;
- Headache;
- Changes in appetite towards its increase or decrease;
- anemia for no apparent reason;
- increased nervousness;
- sleep disorders;
- abdominal pain;
- Perversion of taste.
With liver damage, the clinical picture is complemented by pain in the right hypochondrium, yellowing of the skin and bitterness in the mouth.Filariasis is manifested by signs of cardiac and respiratory failure, toxoplasmosis is accompanied by dysfunction of the central nervous system.Trichinosis affects muscles.
When the genitourinary system is affected by protozoa, signs of infection in women are manifested by frequent urination, discharge from the vagina and urethra, and itching.If an intestinal infection occurs, adults may not experience any symptoms of infection for years.During this time, the parasites multiply and weaken the human immune system, which contributes to the development of chronic and systemic diseases.
Symptoms of the presence of protozoa in the body often include fever, headaches and allergic reactions.One of the first signs of parasites in the body is often a rash on the body and itchy skin.This is due to the human body's reaction to foreign proteins.
Important!
General signs of the presence of parasites in the body in the first stages may resemble intestinal infection, dermatitis, and digestive disorders.
Why are parasites dangerous?
In humans, infection with parasites can cause various reactions and complications.If the invasion is caused by small helminths, the risk of complications is quite low.When infected with large worm species or highly pathogenic protozoa, health damage can be unpredictable.

In addition to certain diseases, which sometimes have a severe course, foreign persons cause serious dysfunction of vital systems.The toxins that parasites release into the blood affect the central nervous system and poison the body.Large helminths have a negative mechanical effect on the organs.Many doctors believe that such tissue injury leads to oncology and tumors.In addition, parasites cause ulcerative lesions of the intestines and stomach, bronchitis and pneumonia, cystitis and pancreatitis, cholecystitis and colitis.
Important!
Sometimes the symptoms of large worms in adults can manifest themselves in the form of an acute abdomen.This happens when worms damage the intestinal lining and develop peritonitis.
Possible sources of infection and preventive measures
There are many ways to become infected with parasites.People are exposed to infections every day.When eating undercooked meat and fish, there is a risk of infection with helminths such as leeches and trichinae.If you don't wash your hands or fruits and vegetables enough, eggs from pinworms, roundworms, toxocara, and other worms can end up in your mouth.When you visit exotic countries, you can become infected with rare parasites such as Guinea worm, malaria plasmodium and trypanosomes.
The infection is transmitted by domestic and wild animals, blood-sucking animals, crustaceans and molluscs as well as ants.Prevention consists in reducing the risk of infection by maintaining hand hygiene and proper heat treatment of meat and fish products.
Important!
Tourism lovers should first study the routes of infection by parasites living in a particular country.
diagnosis
Sometimes it is possible to detect invasion in the body simply by submitting biological fluids and feces for analysis, as well as by studying the anamnesis.However, not all parasites show clinical symptoms and form larvae.Therefore, PCR and ELISA are considered the best diagnostic methods.These are immunological tests that can detect DNA from parasites and antibodies against them in venous blood.
Computer diagnostics are now also very popular, but they only help detect an infection without identifying the specific pathogen.Now hemoscanning of blood is also required, which is carried out by repeatedly magnifying the biological material.
Duodenal intubation helps to find out everything about parasites in the liver.During the procedure, bile is collected and then examined in the laboratory.Echinococcosis at the stage of blistering in the liver and lungs of the body is diagnosed using ultrasound, MRI and X-rays.Intestinal samples can be viewed during a colonoscopy.
Important!
Modern techniques make it possible to detect an invasion as soon as the first signs of infection appear.Therefore, in order to prevent the development of complications, you should consult a doctor as early as possible.
Therapy methods
To combat invasions, they use medical treatment of parasites in the human body, a diet that limits flour, sweets and alcohol, and proprietary techniques.A collection of cloves, tansy and wormwood helps against illness.The method of drinking sweet tea with cognac (1 tablespoon per glass) on an empty stomach and then using a laxative has also proven successful.
Pharmacy drugs against parasites are available in the form of suspensions, tablets, suppositories and solutions for injection.For protozoa, adults are prescribed antiprotozoal drugs.
Parasites need to be treated for up to 5 days.
To remove worms such as roundworms with medication, a single intake of anthelmintic tablets is sometimes sufficient.They destroy the worms from the inside and paralyze their muscles.It is more difficult to cure a person from leeches, echinococci and alveococci.Treatment of the body sometimes takes up to 6 months.
To get rid of parasites forever, you need to take medications according to the regimen prescribed by your doctor.
Important!
Self-medication with medications is strongly discouraged due to the possible worsening of the condition.Sometimes the first signs of death of parasites are manifested by the release of toxins into the blood, which requires additional detoxification therapy.
Treatment with folk remedies
If parasites occur in the body that trigger certain infections such as malaria, toxoplasmosis or trichomoniasis, treatment with home recipes is out of the question.In these cases, qualified medical assistance is required.
Note!
Traditional medicine can be used preventatively or as adjunctive therapy.
To get rid of the infestation, natural remedies based on herbs, flowers and products with a high content of essential oils are used.
They can be treated against parasites:
- wormwood infusion (one tablespoon per liter of boiling water);
- tansy decoction (20 grams of herb per 500 ml of boiling water);
- garlic milk (one clove of garlic per 250 ml of hot milk);
- Onion pulp (chop two onions and mix with vegetable oil);
- Dessert from pumpkin seeds (mix a glass of seeds with half a glass of honey);
- Pumpkin puree (steam and puree 1 kg of pulp in the oven for an hour).
Natural remedies should be taken for at least 10 days, one tablespoon before each full meal.
Reviews on the treatment of parasites
- "I feed my whole family pumpkin seeds. I dry them at room temperature, mix them with jam, condensed milk or honey and serve them with tea. This means no one suffers from parasites."
- "My husband had abdominal pain near his navel for a whole year, suffered from nausea, did a lot of tests and found nothing. Recently a doctor in a paid clinic wrote a prescription for a broad-spectrum anthelmintic, my husband took one tablet and after a week the pain stopped."
- "For prevention, I take an anthelmintic every autumn, as at the dacha I sometimes eat vegetables straight from the bush. The suspension is cheap, tastes good and is well tolerated."